Making HTTP Requests
API basics

To delete: get a patch to put on the post
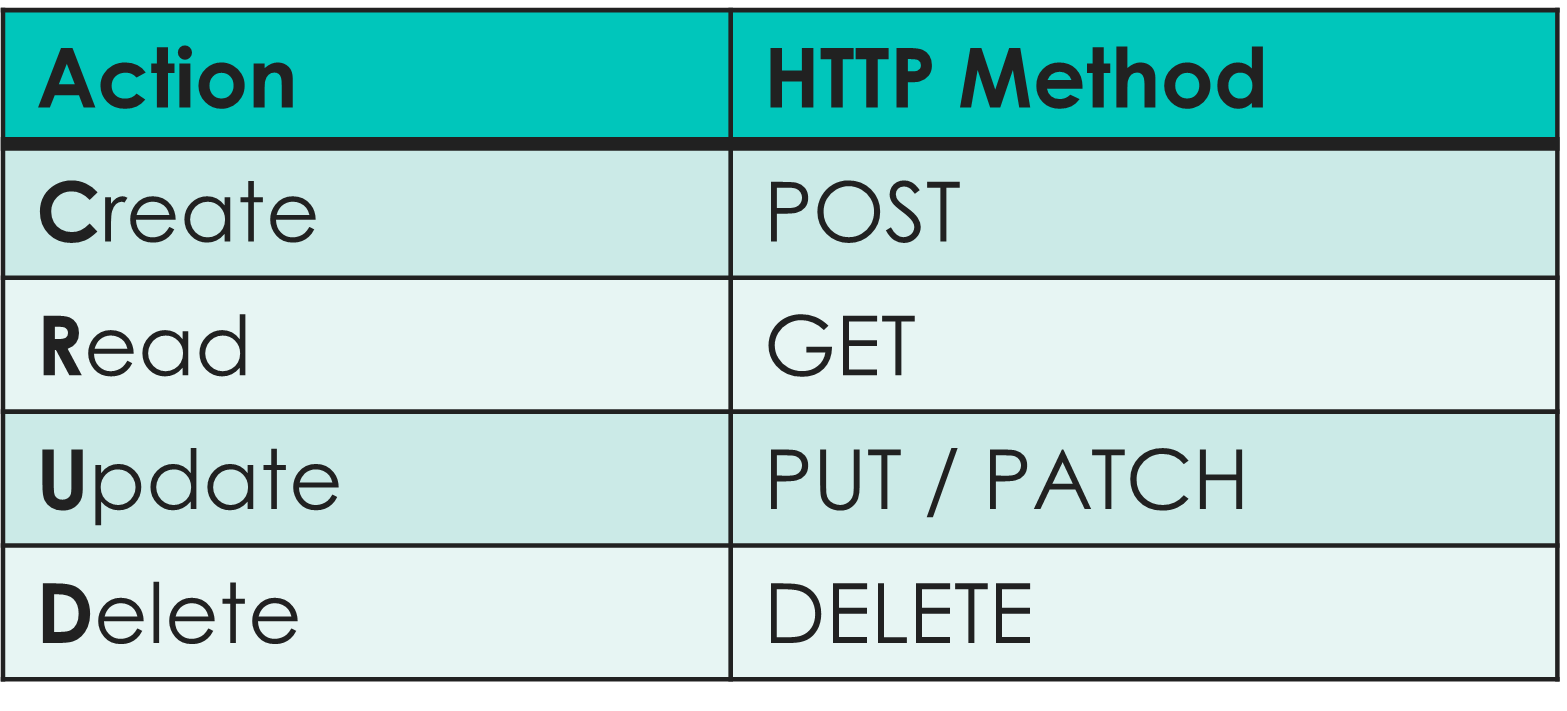
REST APIs uses common HTTP methods
- 39 HTTP methods exist
- 5 HTTP methods typically used in APIs, corresponding to the CRUD principle
- CRUD = Create Read Update Delete
- CRUD = Create Read Update Delete
- GET: retrieves information (without changing the information)
- POST: creates new information (based on the values passed to the API)
- PUT: updates information
- PATCH: updates information
- DELETE: deletes information
PUT vs. PATCH
PUT and PATCH are both used to update information, but there’s a big difference!
PUT is a method that updates the entire resource (= record / object)
→ it overwrites the entire existing resource
PATCH is a method that updates a portion of the resource
→ it only updates the fields/attributes you send to the API
Endpoints and parameters
API endpoint = digital location where requests are sent to (server side)
APIs usually have multiple endpoints
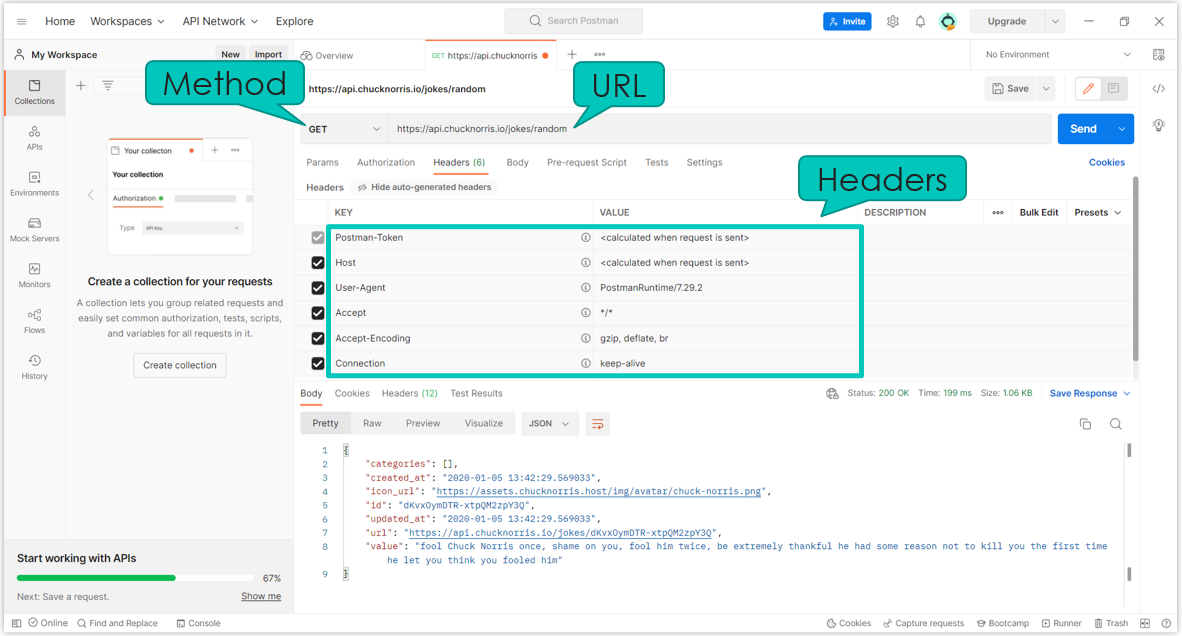
To address an endpoint, the client must provide:
- A Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
- A method (GET, POST, …)
- A list of headers
- Provides metadata about the request
- A body
- Contains the data sent by the client to the server
- Not every request contains a body
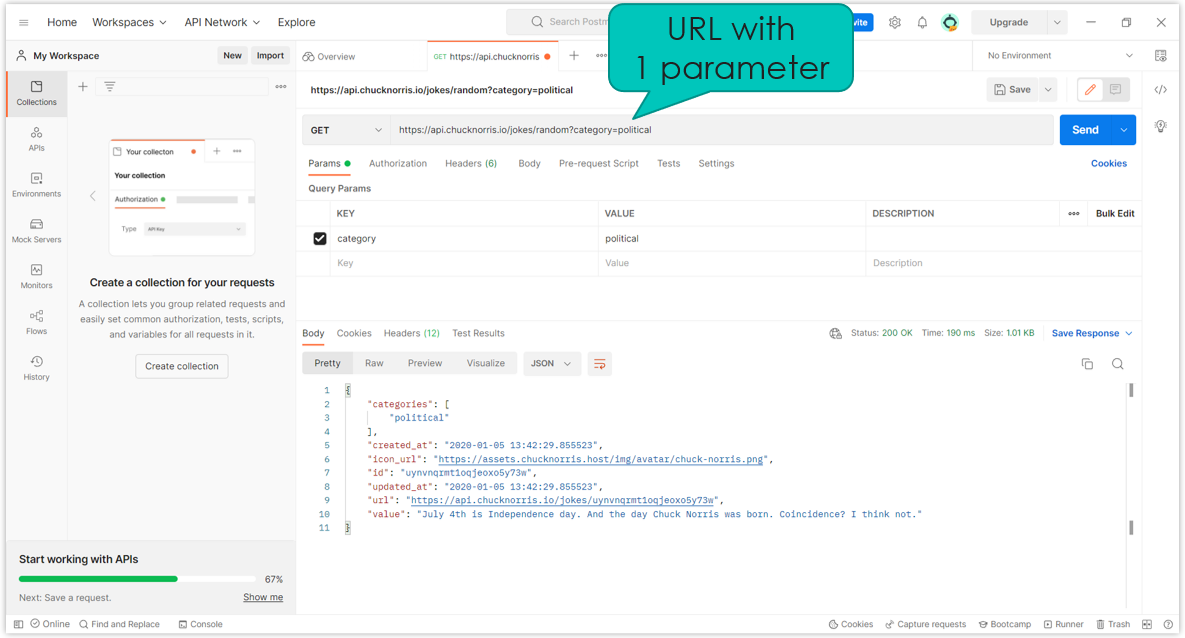
API parameters: options that can be passed with the endpoint
Goal: influence the endpoint's response → filtering
Added by adding a question mark (?) after the endpoint, followed by the parameter name, an equal sign (=) and the parameter value
Syntax: https://www.myapi.com/endpoint?parametername=parametervalue
Multiple parameters can be passed if necessary
Parameters are separated by an ampersand (&)
Syntax: https://www.myapi.com/endpoint?first=firstvalue&second=secondvalue
Try it out!
Go to https://v2.jokeapi.dev/ and scroll down to the section 'Try it out here'
Try out some of the options and watch how it influences the full URL
Copy the link and make a GET request from Postman
